Titanium Valve Grades
Q: Why are cast titanium valves commonly offered in grades different than my wrought pipe?
#materials
A: As previously discussed in Q & A columns, this is not an uncommon practice; certain alloy groups have cast grades that differ in availability from the wrought grades, a situation that is especially true for titanium. For cast chemical process valves, three titanium grades are commonly used: C-3, C-8 and C-12. The cast titanium grades use the prefix C to designate a casting, while the wrought specifications typically use just numbers. For wrought titanium, if you look at ASTM B381 for forgings, 38 grades are listed. Are that many really needed or actually used? Probably not. For cast titanium, 12 grades are listed in ASTM B367, but only the previously mentioned three grades are commonly supplied as valves. Most of the other cast grades are used for light weight and strength in aerospace or medical applications.
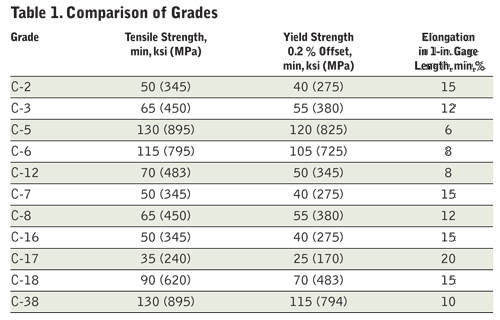
Cast grade C-3 is commercially pure titanium, and like 316 for the stainless steels, C-3 is the most used of the cast titanium grades. Frequently, customers will ask for grade C-2 cast valves because they are familiar with grade 2 for their wrought components such as piping, tubing, plate, etc. The only difference between grade C-2 and C-3 is strength—C-3 is about 35% higher in yield strength than C-2 (Table 1), which helps with the pressure-
temperature rating of the valve. No difference exists between the two grades in corrosion resistance. It’s likely that the wrought producers prefer grades 2 and 7 because the lower strength and better ductility would make these grades more formable; whereas, formability is not a manufacturing concern with castings.
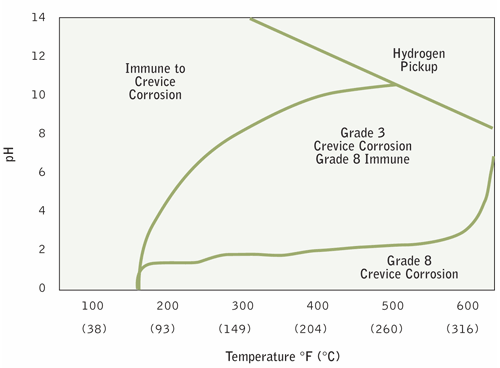
Cast grade C-8 is the palladium stabilized grade of titanium. It is simply grade C-3 titanium with an addition of 0.12% minimum palladium added to enhance general corrosion resistance and improve resistance to crevice corrosion in acid-chloride environments. This small amount of palladium creates a more stable oxide layer on the surface, thus making this titanium grade more corrosion resistant. Grade 7 is the commonly used wrought palladium stabilized grade but C-8 is typically the most offered cast grade. Like with grades 2 and C-3, grade C-8 is about 30% higher in yield strength than C-7, and there is no difference in corrosion resistance between C-7 and C-8. Figure 1 shows brine service and the significant benefit of adding palladium to titanium for increasing its resistance to crevice corrosion.
GRADE C-12
To summarize, there are differences in the availability between cast and wrought grades, and it is not always necessary to match the valve alloy to the piping alloy. However, if you feel that titanium grades C-2 or C-7 are actually needed, valve manufacturers should be able to supply those grades.
THOMAS SPENCE is director of material engineering for Flowserve Corp. (www.flowserve.com), Dayton, OH. Reach him at tpensce@flowserve.com.
RELATED CONTENT
-
Cobalt-based Alloy 6 Materials and Boiler Feedwater Service
Q: I’ve heard that cobalt-base Alloy 6 materials should not be used in boiler feedwater service.
-
Metal Additive Manufacturing: the Evolving Road to Adoption and Standardization
Greater knowledge and acceptance of metal AM valve components—especially with various standardization efforts underway—will spur the technology’s growth.
-
The Materials That Make Up Valves
EDITOR’S NOTE: Materials used in the manufacture of valves and how they perform in different applications is a topic of huge interest to everyone who works with valves.








 Unloading large gate valve.jpg;maxWidth=214)

